Chainsaw: The Roaring Power in Modern Forestry and Emergency Operations
The chainsaw, a portable power tool driven by a gasoline engine that rotates a cutting chain at high speed, has revolutionized timber harvesting, landscape management, and disaster response since its inception in the early 20th century. It stands as an iconic symbol of humanity’s ability to harness natural materials.
Core Components and Technical Principles
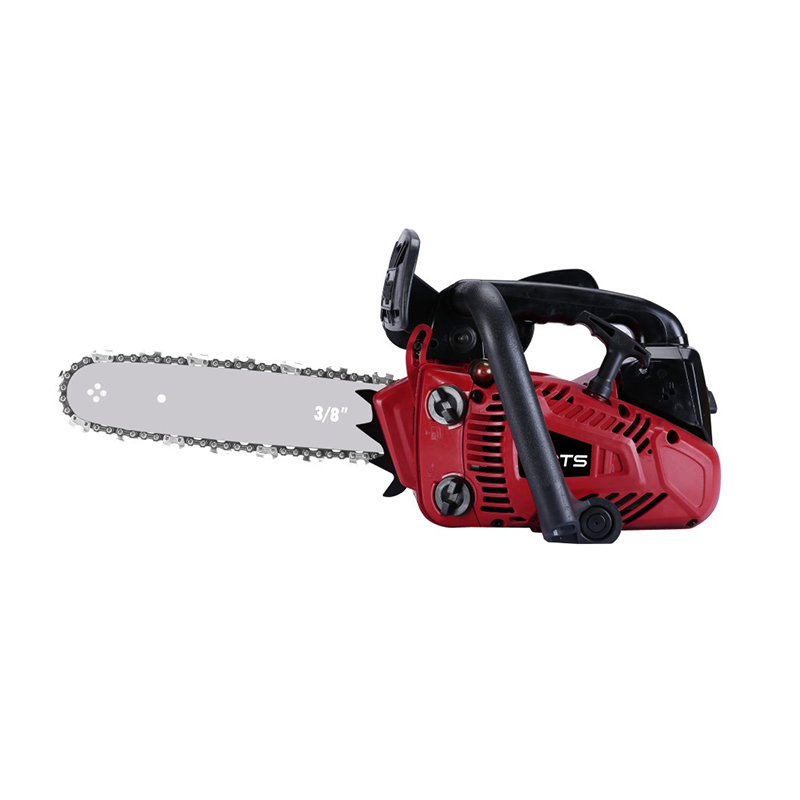
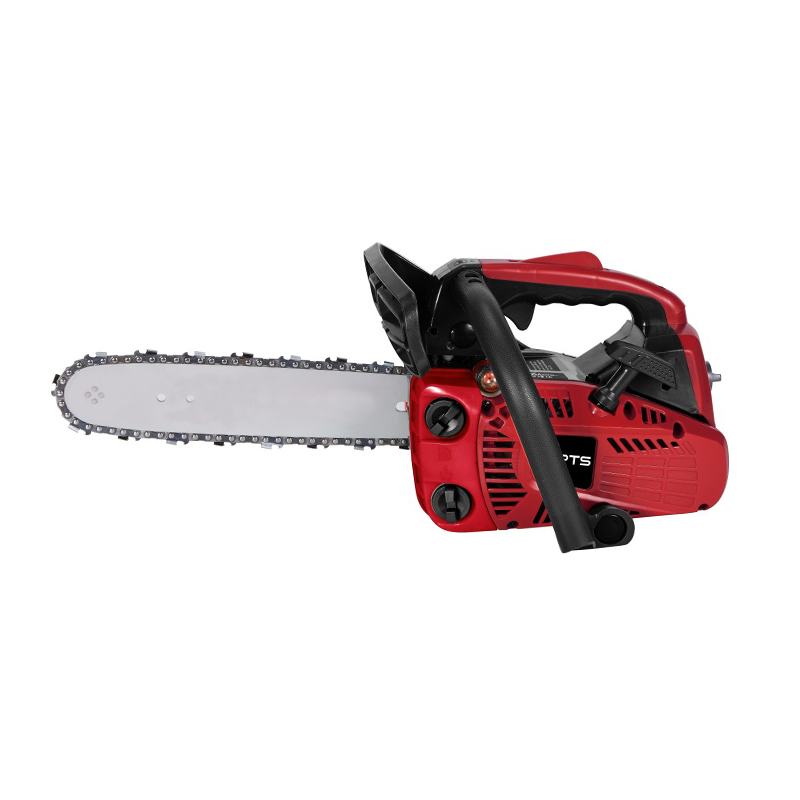
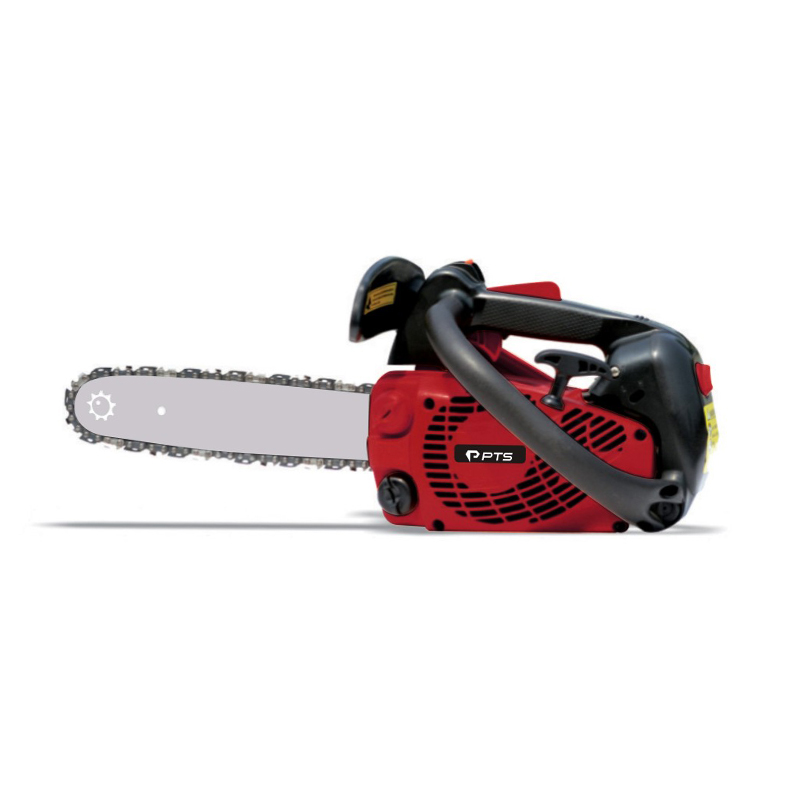
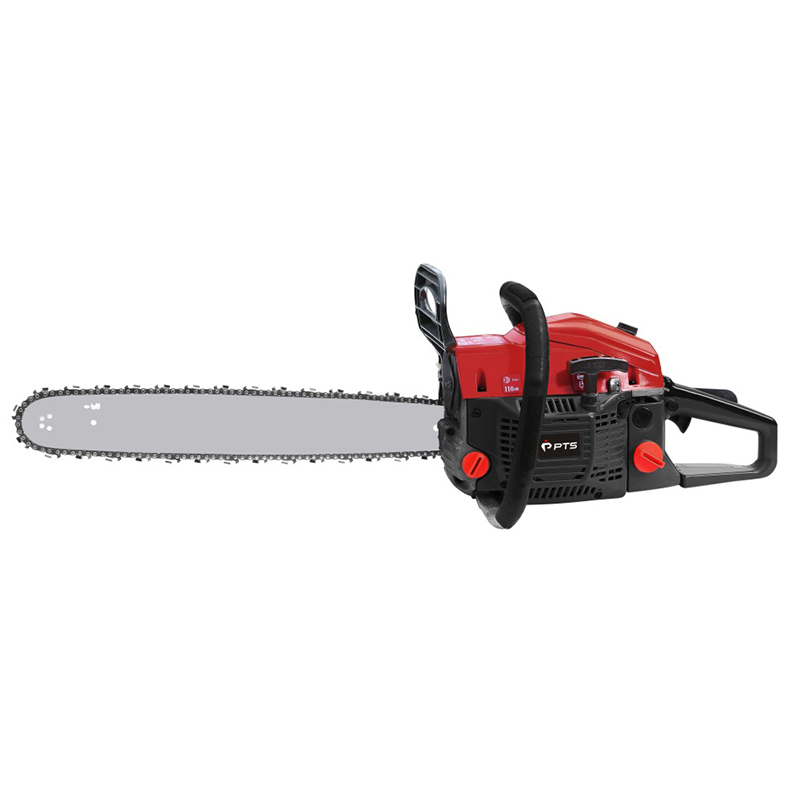
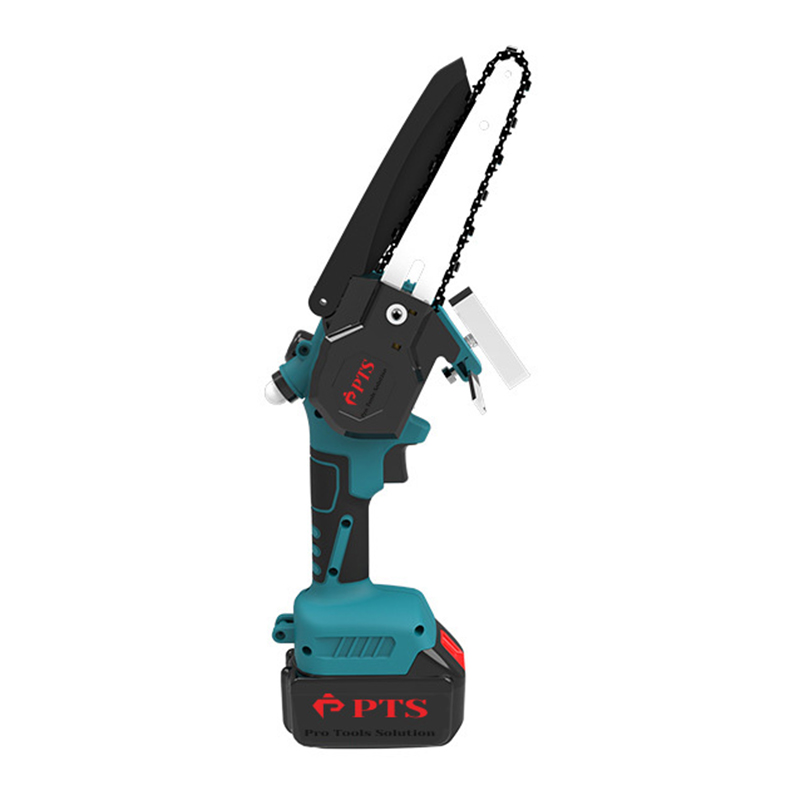
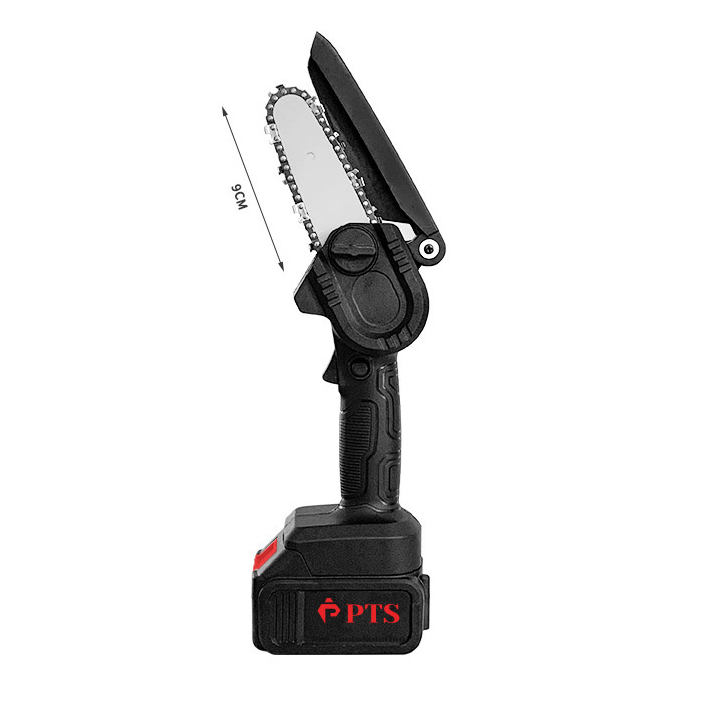
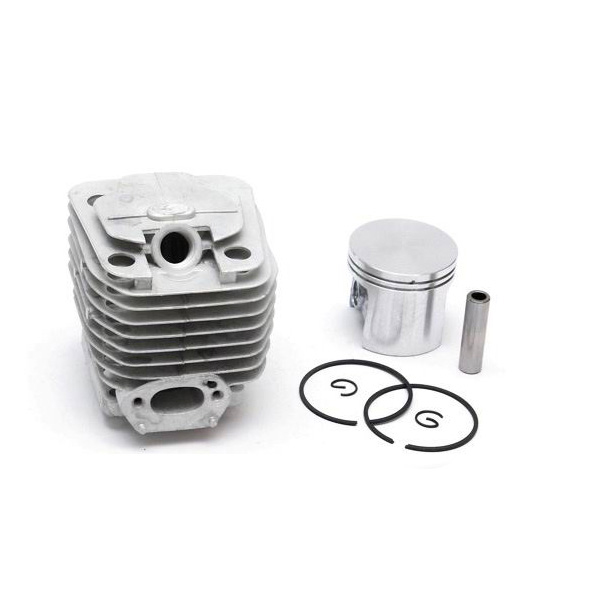
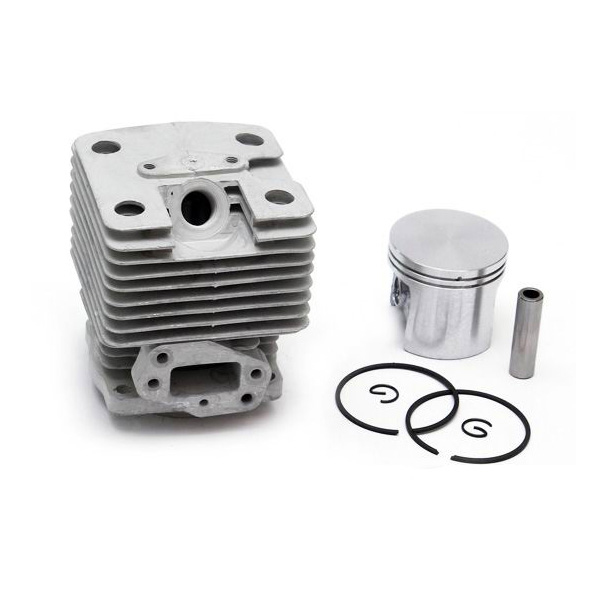
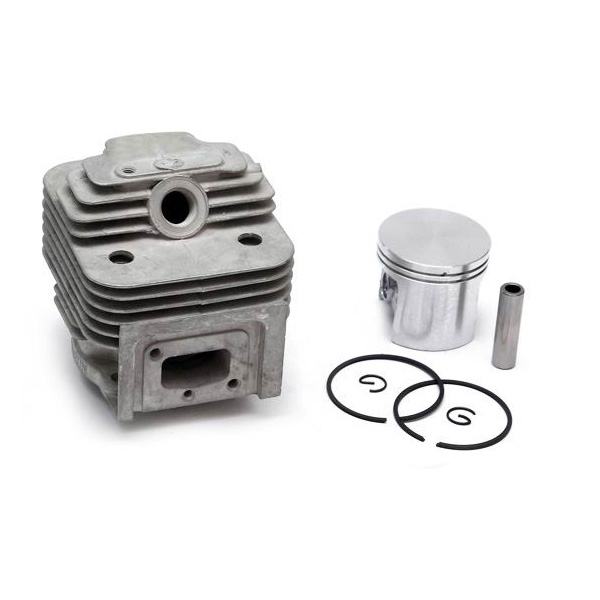
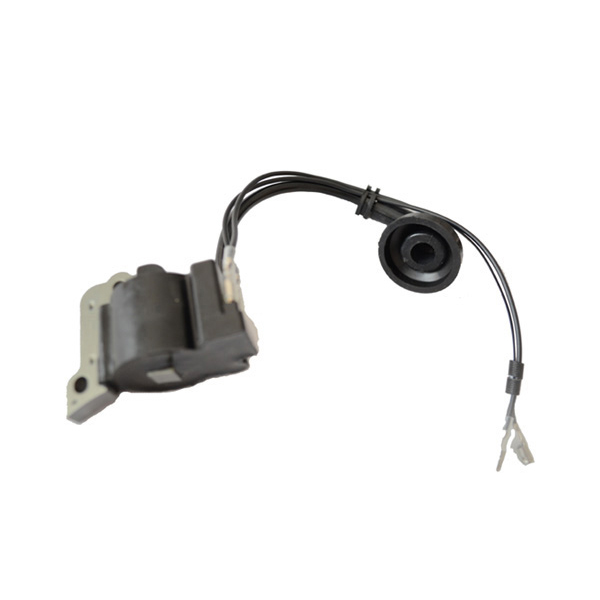
At its heart, a chainsaw consists of a two-stroke gasoline engine, a cutting chain, and a guide bar. The engine burns a mixed fuel (a specific ratio of gasoline and oil) to generate power, transmitted via a centrifugal clutch to a drive sprocket. This drives a chain embedded with sharp cutting teeth along the edge of the guide bar at speeds exceeding 9,000 RPM. The design balances lightweight construction with high power density—modern chainsaws can weigh as little as 4 kg while delivering over 5 horsepower.
Classifications and Applications
Forestry-Grade Chainsaws: Large displacement (60cc+), long guide bars (45cm+), designed for sustained heavy-duty logging.
Gardening-Grade Chainsaws: Medium/small displacement (30-50cc), lightweight and agile, ideal for pruning and light woodcutting.
Emergency Rescue Chainsaws: Enhanced safety features for rapid clearance of fallen trees and debris post-floods or earthquakes.
Golden Rules for Safe Operation
The high-risk nature of chainsaws demands strict adherence to safety protocols:
Personal Protection: Wear cut-resistant chaps, safety goggles, noise-canceling earmuffs, and anti-slip gloves.
Operating Posture: Stand with feet firmly apart, grip handles tightly, and avoid contact with the chain tip (to prevent "kickback").
Environmental Awareness: Clear the work area of obstacles and plan escape routes for tree felling.
Critical Maintenance Practices
Chain Lubrication: Check oil flow before each use; ensure automatic lubrication systems function.
Tooth Sharpening: Dull teeth increase fuel consumption by 30%; regularly file cutting angles with a round grinder.
Air Filter Cleaning: Clean filters immediately after woodland use to prevent dust clogging and engine overheating.
Future Evolution: Eco-Friendliness and Intelligence
With the EU’s Stage V emission standards, electronic fuel injection (EFI) is replacing carburetors, reducing harmful emissions by 30%. Lithium-ion chainsaws (e.g., 56V platforms) are gaining ground in urban landscaping, while innovations like laser-guided cutting and auto-tensioning systems redefine precision operations.
The roar of a chainsaw is not just an industrial footnote but an ongoing dialogue between nature and engineering. Mastering its power requires respecting its risks—this is the ultimate philosophy of the chainsaw.
Previous:No
 Back
Back